A patient with a problem such as varicose veins of the lower extremities should not hesitate to consult a doctor and start treatment. An experienced specialist will conduct a thorough study and decide which therapy tactic is best: conservative or surgical treatment. If for some reason the medication does not have the desired effect on the patient's blood vessels, doctors already prescribe surgical intervention that can help unconditionally.
Indications and whether the operation is generally necessary
Surgery to remove varicose veins is a radical approach to the treatment of pathological veins, so the indications will be appropriate.

The operation will be justified in the following cases:
- common varicose veins of the lower extremities, visible to the naked eye;
- persistent acute swelling of the legs, discomfort, pain and a feeling of heaviness in the legs or elsewhere depends on the localization of the pathological process;
- a direct threat that existing varicose veins in a particular part of the body will be complicated by a more dangerous disease (e. g. , thrombophlebitis, trophic ulcer, or pulmonary embolism).
He will be able to determine in a direct conversation with the doctor whether it is worth performing the operation and what kind of surgical interventions are generally available.
Contraindications to surgical treatment of varicose veins
Despite the strong indications, there are many cases in which surgery to remove varicose veins in the legs is not possible. For example, if a patient has the final stages of varicose veins, surgical treatment will not always be possible. In such cases, doctors pay attention to medication, but can not help enough.
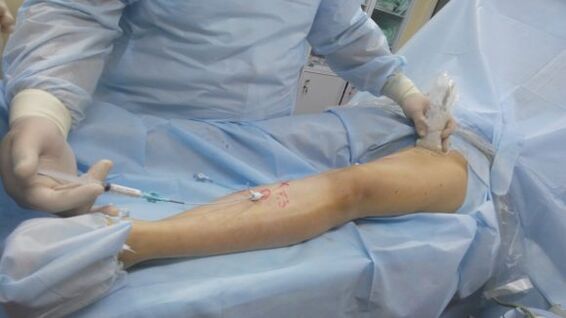
A number of other mandatory contraindications:
- presence of skin diseases in the affected vascular area, such as eczema, pyoderma, dermatitis, etc.
- severe diseases of the cardiovascular system - hypertension, coronary artery disease, heart failure;
- acute inflammatory process in the vein (phlebitis);
- previously transferred thrombosis or pulmonary embolism;
- an active process that destroys atherosclerosis;
- old age;
- pregnancy period.
Patients should remember to inform their attending physician if they are taking medication for other illnesses.
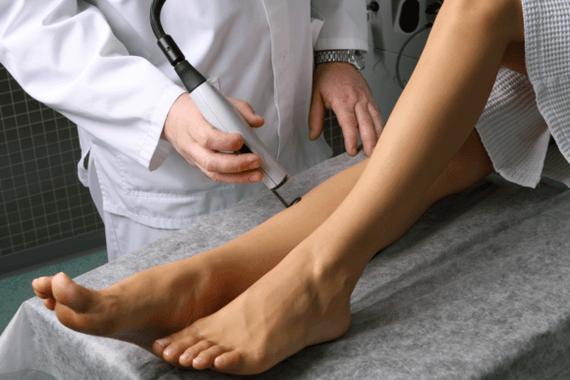
Sclerotherapy techniques
Sclerotherapy is a procedure in which a special substance is injected into the affected vessel and causes the vessel to further narrow and grow. The main advantage of this method is that the procedure does not require any incisions or surgery.
The essence of the procedure is as follows: with the help of a syringe, the doctor injects a substance that causes multiple sclerosis in the pathological vessel. At one stage of sclerotherapy, a specialist injects two to ten such needles. The effect is not visible at the same time - usually 2-8 weeks, and such a procedure takes several sessions. Under the influence of sclerosant, the vessel gradually narrows, then becomes overgrown and disappears.
There are two types of manipulation:
- Microsclerosis. In the early stages of varicose veins, it is justified when the smaller superficial veins are involved in the process. In such cases, the amount of sclerosant required is minimal.
- Echosclerosing. To most accurately determine the location of deep varicose veins, it is performed in deeper veins using duplex scanning.
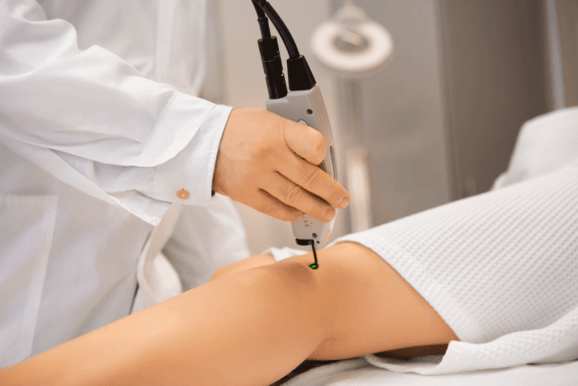
Laser coagulation
Laser surgery for varicose veins is by far the most popular. This is because the procedure itself is performed under local anesthesia, does not require large incisions and tissue trauma, and has an immediate effect.
The vascular surgeon should explain in detail how the operation is performed, but generally the essence is to insert a special laser light guide into a diseased vessel. A laser beam with its own wavelength passes through this device and affects the walls of varicose veins. Under its action, the ship clots and clogs.
If the patient has varicose veins of the leg or groin area, this method will be justified. In addition, laser coagulation will be more effective in large vessels, so the use of this technique in case of damage to small vessels is unreasonable.
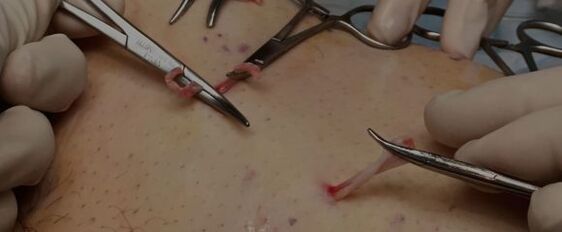
Ligation of blood vessels
Vascular ligation is a more radical operation for varicose veins in the legs that require a wide incision and direct surgical intervention.
The operation is performed on more legs than veins in the pelvic region. Safenosis vascular closure technique will be effective. The vascular surgeon reaches the vessel shown at the point where the saphenous vein joins the femoral artery. Then, the surgeon performs a bandage with special threads.
Pelvic vein surgery can be performed in women. In this case, the ovarian vein is reached and closed.
Removal of dilated vessels
The most common and proven method of surgery is phlebectomy. Doctors do this almost every day and are more profitable than laser coagulation or sclerotherapy. For varicose veins, such an operation is performed under general anesthesia or with epidural anesthesia.

To remove the dilated vessel, the surgeon needs an incision only 0. 5-1 cm long. The surgeon closes, closes and removes the vein, allowing access to the area with varicose veins.
Miniphlebectomy is distinguished as a subtype of this intervention. Unlike conventional phlebectomy, the surgeon needs more holes than incisions to reach the vessel. This operation is effective for affecting small superficial vessels. The main advantage is that it does not leave any traces and cosmetic defects.
Don't peel
Dressing is one of the subtypes of phlebectomy, during which a special probe is used to remove the vein. As with the removal of a simple varicose vein, the surgeon makes an incision in the saphenous vein and reaches the vein. Then the doctor makes another incision - in the middle or lower leg area.
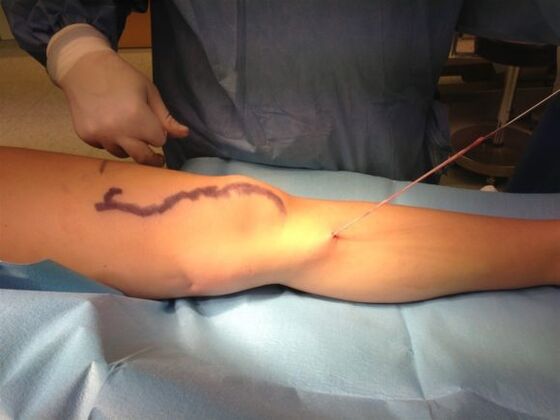
A special probe is applied through the upper entrance to the great saphenous vein - the excretory probe. The surgeon pre-wraps the mouth of the adjacent vessels. The probe passes through the lower incisions along the entire length of the vessel, after which it is used to remove the vessel.
There are several types of manipulation during peeling:
- Short peel. Not the whole vessel, but only a certain area that is subject to the process of varicose veins is removed.
- General. Such an operation for varicose veins of the lower extremities allows you to get rid of a large area of diseased veins and prevent further relapses.
Outcomes of surgery and rehabilitation
Surgery for varicose veins can have side effects and lead to various complications. They should be distinguished by the type of intervention:

- After sclerotherapy, the patient may experience itching, burning, discoloration of the skin, and edema at the injection site. An increase in body temperature and the formation of general weakness are possible. Following the rules of the postoperative period, the symptoms disappear in a few days.
- After laser coagulation, the patient may experience a feeling of tension in the thigh area, minor bleeding, and an increase in body temperature. With proper treatment, the symptoms disappear within a week.
- Vascular occlusion can be complicated by trauma and bleeding during the operation itself.
- Phlebectomy and peeling can damage the nerves in the skin. This may be accompanied by loss of sensation, numbness in the legs, pain in the incisions.
There is a common complication for all surgical treatments - thrombosis. This is a dangerous process, but it is very unlikely to occur as a result of any operation.
To prevent the above complications and to shorten your rehabilitation period as much as possible, you should follow the recommendations for the care of your health and blood vessels in the postoperative period.
Following the rules of the postoperative period, the symptoms disappear in a few days.
There are a number of pros and cons that experts recommend to follow.
- Immediately after the operation and in the first week after it is necessary to wear special compression underwear - it can be in the form of socks, tights, socks, and for this purpose you can use an ordinary elastic bandage.
- Eliminate bad habits - alcohol consumption, smoking, drug use.
- Avoid baths and saunas, as well as very hot baths.
- You can not perform any cosmetic procedures and apply various cosmetics at the site of the operation.
- Avoid strenuous physical activity. If the patient is involved in any sport (especially heavy) before treatment, heavy loads should be forgotten for at least 5-8 weeks after surgery. If it is possible to continue intense sports in the future, you should consult your doctor.
- Perform daily preventive exercises for no more than 15-30 minutes.
- Follow a phlebologist's prescription to take medication - take regular prophylactic anticoagulants, phlebotonics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, thrombolytics and other medications.
In general, all these operations have good reviews from both doctors and patients. Only the attending physician should decide which approach to treatment is appropriate for a particular patient.























