Varicose veins or varicose veins of the lower extremities is the primary varicose transformation of superficial veins of the lower extremities, with "bumps" or "knots" on his feet.
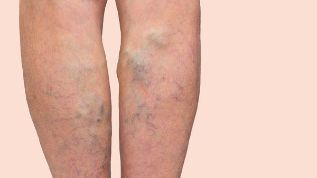
Varicose veins disease is very widespread around the world. The frequency reaches Its 60 % of the adult population depending on the country. Interestingly, the citizens of Loviisa on the African continent, as well as the Asia-Pacific region suffer from varicose veins much less than of people and European countries and the USA.
Context without concrete reasons for varicose veins of the lower extremities is customary to talk about its risk factors, in other words, what this increases the likelihood of developing the pathology (the property or characteristic of the human body potential effects in the body). Common risk factors, consider the age, female gender, obesity and heredity. Typical "portrait" of the patient's symptoms of varicose veins — of women in the state of menopause, which is a excessive body mass index, take and multiple pregnancies childbirth in anamnesis.
Symptoms of varicose veins in the legs
In the vast majority of cases, varicose veins can be identified even without any special medical training. A clear objective sign of pathology — the appearance of "bumps" or "nodes" of the lower extremities, the skin when over them is usually not anything in particular stands out in color. Blue veins are generally not a disease in its literal sense, although often that patients (mostly women) harm the aesthetic character.
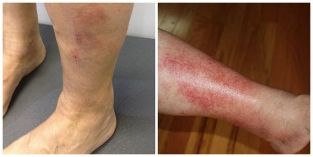
However, in advanced cases, varicose veins may be associated skin discoloration due to venous eczema, which occurs in different itchy skin rash (blisters, nodules) and redness.
These means of, as well as swelling of the legs, which will not disappear for the night time show the formation of chronic venous insufficiency.
What subjective symptoms of varicose veins, key role in the environment, their non-specificity. The complaints of the disease may indicate, and can be a sign of overloading of the venous system of the lower extremities. Most often patients suffering from pregnancy, edema and mild non-localized aching pain in the calf. Sometimes there is pain in the area of varicose veins complaints and fatigue in the legs.
Burning, tingling, muscle cramps at night or restless legs (unpleasant sensations in the legs at rest, when he movement to ease this pain) were the most commonly reported neurological disease, for example, radicular syndrome, and should be taken into account with caution.
Pathogenesis of varicose veins in the legs
Pathogenesis of varicose veins of the lower limbs is quite complex and diverse. The most important role in the mechanism of the disease development of call and harm the walls of the valves in the veins. As a result of their irregular Work form a reverse blood flow (reflux), so there is a loss of the endothelium (the inner lining of the vessel), which is involved in inflammation.
If the pathological process involved in the middle and inner layers of the venous wall, there is a proliferation of connective tissue from the muscular layer of the vein, and then the atrophy, which leads to a gradual destruction of the collagen of the vessel. These features happen to interfere with the elastic in Vienna, to promote the further expansion and its snow spiral twisting along. At the same time, no similar changes observed in venous valves.
The key role of the environment, that the venous visible "bumps" and "node" are usually the result of English the invisible source of the varicose great saphenous vein. In most cases, this is a big, sometimes small saphenous vein. The above-mentioned pool in the veins of these changes and lead to varicose veins.
Complications of varicose veins in the legs
Complications of varicose veins should include the trophic disorders (venous ulcers), thrombosis or varicose changed veins (thrombophlebitis) bleeding or varicose veins "bumps" and "nodes".
Trophic disorders are the spot the result of disease, progress of treatment, it will take years and use for decades. They start with cutaneous manifestations of hyperpigmentation (brown spots), venous eczema and lipodermatosclerosis (seal skin).
Of these the most Important localization changes is the tibia, although venous eczema occur in any can area varicose veins, including the thigh. Depending on the source of varicose veins (great or small saphenous veins) venous disorders can be localized to either the inner or outer surface of the lower third leg, respectively. Malnutrition of the soft tissues is the formation of venous ulcers in place before the changes. Ulcers are single or multiple, irregular shape, sloping edges and a flat, smooth bottom. The key role of the environment, scant discharge, often purulent character. The wounds are included and itching pain. Venous ulcers is noteworthy that there is a long (months) and frequent recurrences.
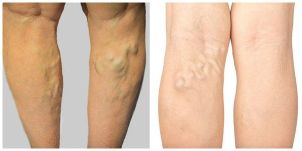
Thrombophlebitis or superficial vein thrombosis is not to be confused with deep vein thrombosis. In the second case the situation is more serious. However, thrombotic lesions varicose veins-symptoms are very unpleasant. Region thrombosed vein painful threadlike form a seal, it is characterized by redness, local rise in temperature and increased sensitivity, sometimes the seal to restrict the movement of limbs. The clinical picture or, more reminiscent of a wound abscess.
Thrombophlebitis can be particularly dangerous if you take them up in nature and enters the superficial system to the deep. In this case, it can develop into pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis.
Bleeding varicose veins very scary look, as because of the venous high pressure stream of blood strong enough. In some cases, this can lead to significant blood loss.
The diagnosis of varicose veins in the legs
The diagnosis of varicose veins of the lower extremities do not usually cause any problems. A key feature of the disease is in English venous "bumps" and/or "nodes". Despite the excessive development of the subcutaneous fat of the lower limbs to see them can be difficult.
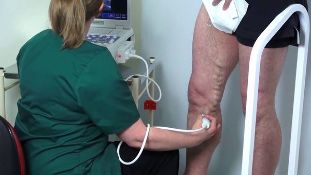
To further confirm the diagnosis using various methods of instrumental diagnostics, the leading, which is ultrasonic duplex scanning (USDs). It allows you to quickly, accurately and safely determine the source of varicose veins, to assess the size and structure of the training vessels of the venous valves, the scale distribution of the return current of the blood of the son, and recognize English blood clots. Deep and looks in the Same superficial venous system. To perform the study should be in the standing position or, if the patient's condition does not allow to sit unfortunately on their feet. The study in the supine position can cause errors and determining the reflux of blood clots.
On and the valves a function of the length of the return current of blood is used for:
- compression here by hand pressure on different segments of the lower extremities;
- sample straining (Valsalva test);
- simulated walk;
- welcome to the paraná is easy to try-remove the patient's equilibrium, whose purpose is to call the tension in the calf muscles.
Summary ultrasound duplex study of lower limb veins is necessary in the form of a statement confirmed and graphics, by drawing a "vein map". The results of the study provide valuable help when planning the treatment. However, they must be taken account of in vain together with clinical data, such as changes in the ultrasound pattern, without objective signs of the disease (varicose veins), should be considered functional (i.e., not related to pathology of the veins). It is also a key role of the environment, that does not necessarily ultrasound scan done, if the diagnosis is clear and if the patient is not planning to surgical treatment of varicose veins.
There are other methods of diagnosis:
- Doppler ultrasound — Doppler ultrasound (not to be confused with the usd effect);
- plethysmography;
- radiopaque venography;
- radio telegraphy;
- computed tomography (CT);
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- thermal imaging;
- intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) is a new method.
Treatment of varicose veins in the legs
The primary goal of treatment of varicose veins of the lower limbs is to remove all the malfunctioning veins. This is possible in vain with the help of invasive procedures. There are three methods:
- Deleted — combined phlebectomy short vein Stripping, mini phlebectomy, a dissection of the perforating veins;
- "Bonding" — sclerotherapy, mechanochemical ablation, cyanoacrylate destroyed;
- "The brewery" — endovenous laser or radiofrequency ablation.
To achieve the goal of treatment is to perform two functions: remove the source of varicose veins (so-called. vertical reflux) and to remove the varicose veins. For a long time was the most commonly used method for combined phlebectomy. Its technical construction includes two steps:
- Ligation anastomosis — the connection to the great saphenous vein with the common femoral vein (crossectomy);
- Remove trunk of the saphenous vein with the probe (Stripping).
This is a radical intervention and has a number of drawbacks inherent in any training: use the camera I need for anesthesia, English incision, stitches yes, a significant rehabilitation period and increased in comparison with other methods the risk of complications.
However, about twenty years ago there was a "phlebology revolution." It became possible thanks to the widespread introduction of ultrasound appearance and exquisite techniques — endovenous thermal ablation. Its essence lies in the effects of high temperature of the vein wall from the inside. This is achieved by a laser radiation (EVLO) or RFR (RFO), "safariways" the lumen of the vein.
Vienna this stop training immediately, and then gradually corrected. This method allows you to place the incision, fast, efficient, pleasant and safe aesthetically vertical to eliminate reflux without the need for rehabilitation. Is bright representative of "office surgery", endovenous thermal ablation ten years is considered the most optimal method of treatment of varicose veins worldwide.
Sclerotherapy (bonding affected veins by injecting a substance) also found wide use in the removal of varicose veins. However, in order to achieve the desired result requires careful selection of patients, because of the increased table relapse.
Conservative treatments including compression therapy, phlebotrophic drugs and local medicinal forms (gels, ointments), are purely auxiliary in nature, that affect mainly the symptoms of varicose veins removed without the source.
Forecast. Prevention
Taking into account the modern methods of treatment, the prognosis of varicose veins is favorable. Even the most seemingly advanced cases to remove the varicose changed veins lead to the rapid improvement of the patient's condition.
However, when planning treatment it is important to assess its risks, as with any intervention still carries potential adverse effects. The duty of a doctor is to minimize their likelihood. Before the manipulation should be discussed with the aspects of patients with all, concerning the work and for her to get signed consent.
All adverse events can be divided into risks associated with surgery, including anesthesia risks for the patient.
Risks of surgery can be small, for example, inflammation (phlebitis) is "cooked" or sklerozirovanie veins, after which and the seal projections of moderate pain. Can be skin areas with reduced sensitivity, and skin hyperpigmentation. Side effects are All these transient over and usually quite quickly without any consequences.
Big complications are deep vein thrombosis, allergic and toxic reactions to the anesthetic. They occur very rarely, but one patient, who suffered such a complication, the case is 100%, even though the statistics of 1 case per 10,000 operations.
Prevention of venous thrombosis is primarily based on the calculation, the table is the so-called scale-point scale using table Caprini. It includes a variety of risk factors, which is gradation. Into account each factor and eliminate the total score to determine the degree of the table, and therefore its prevention. The most important means for the prevention of venous thromboembolism following:
- reducing the morbidity of the training;
- early activation of the patient;
- support socks;
- pharmacological prophylaxis, i.e. the task according to the testimony of anticoagulants — drugs that thin the blood.
As for the prevention of varicose veins, simply it does not exist, because it is not yet clear, the main cause of the pathology, which can affect and thus prevent special needs in the onset. Related, and quite often the recurrence of varicose veins after any type of intervention. However, taking into account all the advantages of mini-invasive treatment, this is not a significant problem. To maintain the foot quite simple, the main time refer to phlebologist























